Acute Coronary Syndrome Treatment Guidelines American Heart Association
Acute coronary syndrome treatment guidelines american heart association. Medications for the Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome. Despite the fact that several studies have documented this association hyperglycemia remains underappreciated as a. In patients with STEMI managed with PPCI there is a.
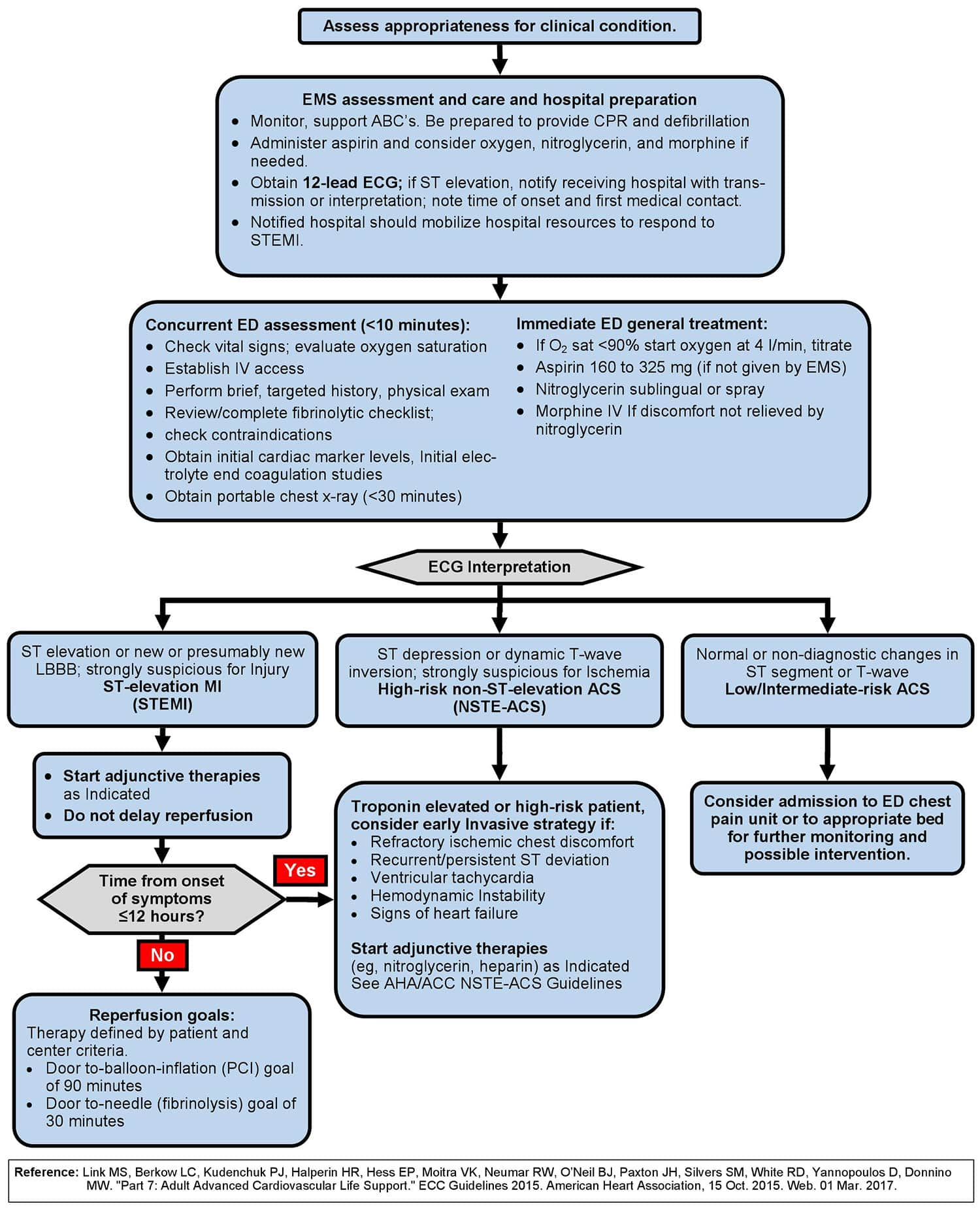
The 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC for the evaluation and management of acute coronary syndromes ACS are intended to define the scope of training for healthcare providers who treat patients with suspected or definite ACS within the first hours after onset of symptoms. Ment followed by a 75 mg daily dose for up to 8 days in. Unstable angina or sometimes referred to as acute coronary syndrome causes unexpected chest pain and usually occurs while resting.
Age is an important determinant of outcomes for patients with acute coronary syndromes ACS. The most common cause is reduced blood flow to the heart muscle because the coronary arteries are narrowed by fatty buildups atherosclerosis which can rupture causing injury to the coronary blood vessel resulting in blood clotting which blocks the flow of blood. All patients being transported for chest pain should be managed as if the pain were ischemic in origin.
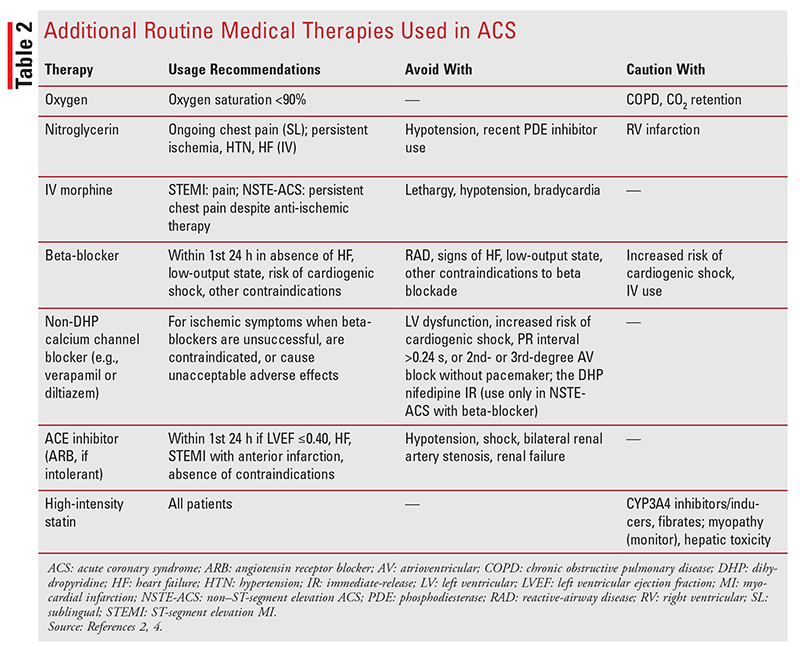
Two new drugs added to heart failure guidelines. Heparin low-molecular-weight heparin LMWH or un-. Reduction in combined event rate cardiovascular mortal-.
We evaluated the application of the 2018 American College of CardiologyAmerican Heart Association cholesterol management guideline recommendations for additional lipid-lowering therapies in patients with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and residual dyslipidemia despite maximum tolerated statin therapy who were enrolled in the ODYSSEY OUTCOMES trial Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcomes After an Acute Coronary Syndrome During Treatment. Guidelines revise how long certain heart disease patients should receive a blood-thinning drug combination. Reasons include limited trial data to guide the care of older adults and uncertainty about benefits and risks particularly with newer medications or invasive treatments.
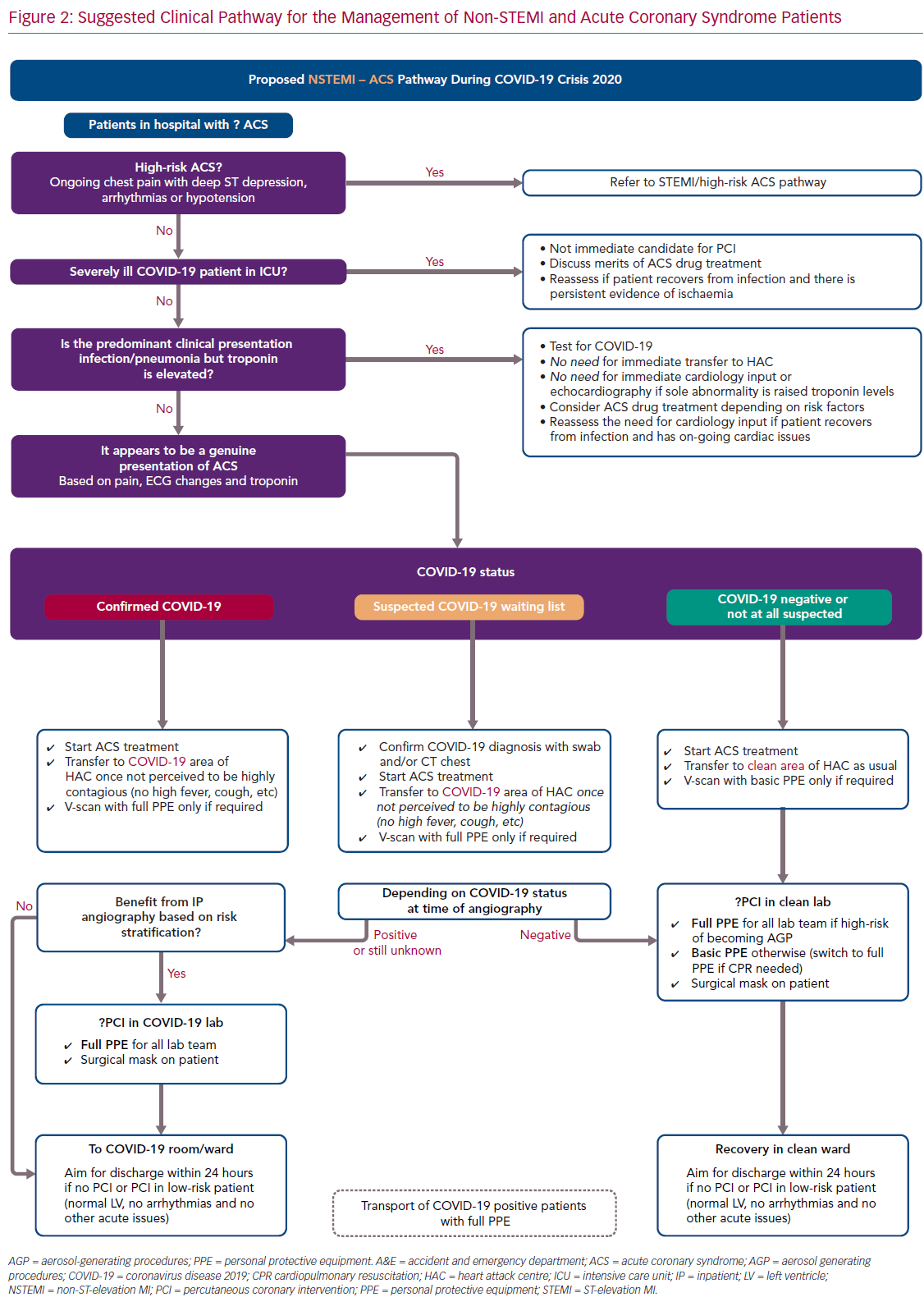
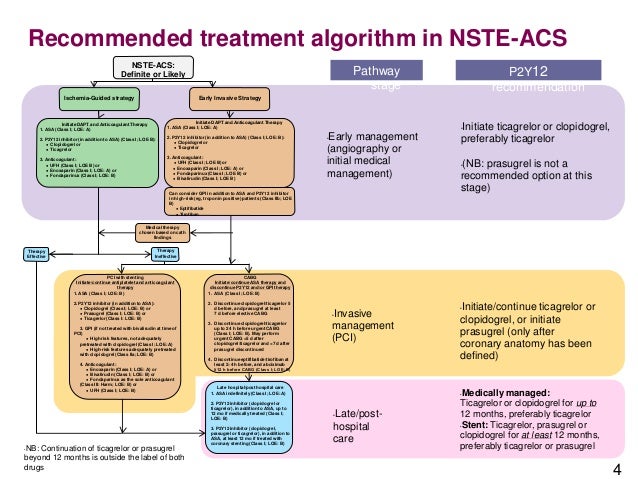
2014 AHAACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With NonST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes. A report of the American College of CardiologyAmerican Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Level of Evidence LOE And Class Matrix Amsterdam E.
Compliance with guideline-directed therapy in diabetic patients admitted with acute coronary syndrome. 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines Update for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Circulation.
The most common cause is reduced blood flow to the heart muscle because the coronary arteries are narrowed by fatty buildups atherosclerosis which can rupture causing injury to the coronary blood vessel resulting in blood clotting which blocks the flow of blood.
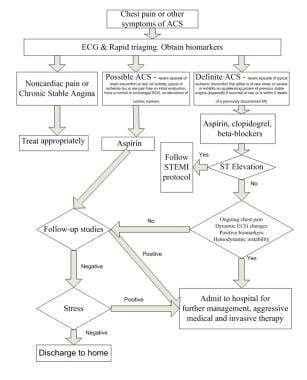
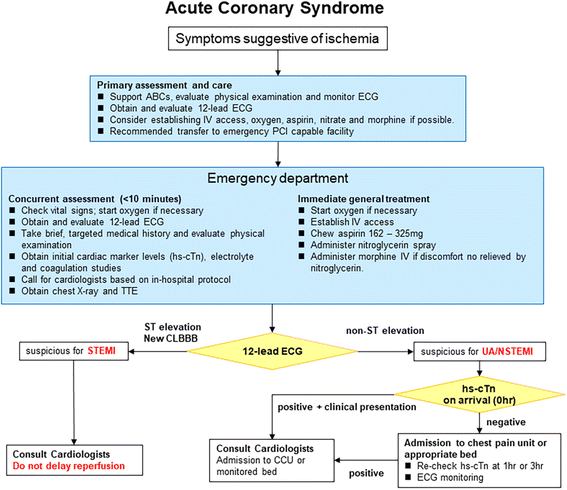
The American Heart Association explains that acute coronary syndrome is an umbrella term for situations where the blood supplied to the heart muscle is suddenly blocked such as heart. 2014 AHAACC Guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes. A report of the American College of CardiologyAmerican Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Two new drugs added to heart failure guidelines. 2014 AHAACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With NonST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes. The term acute coronary syndrome ACS refers to any group of clinical symptoms compatible with acute myocardial ischemia and includes unstable angina UA nonST-segment elevation myocardial infarction NSTEMI and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction STEMI. PAD patients should take statins blood thinners. An initial intravenous loading dose of. All patients being transported for chest pain should be managed as if the pain were ischemic in origin.
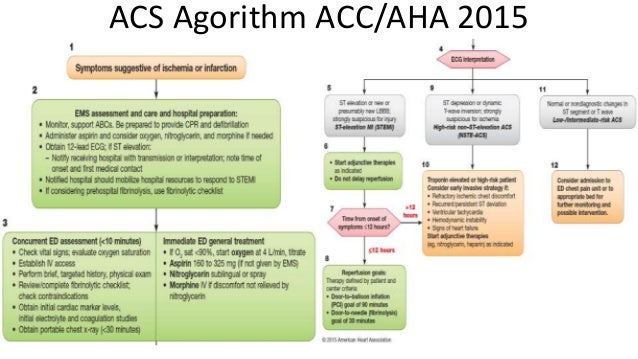
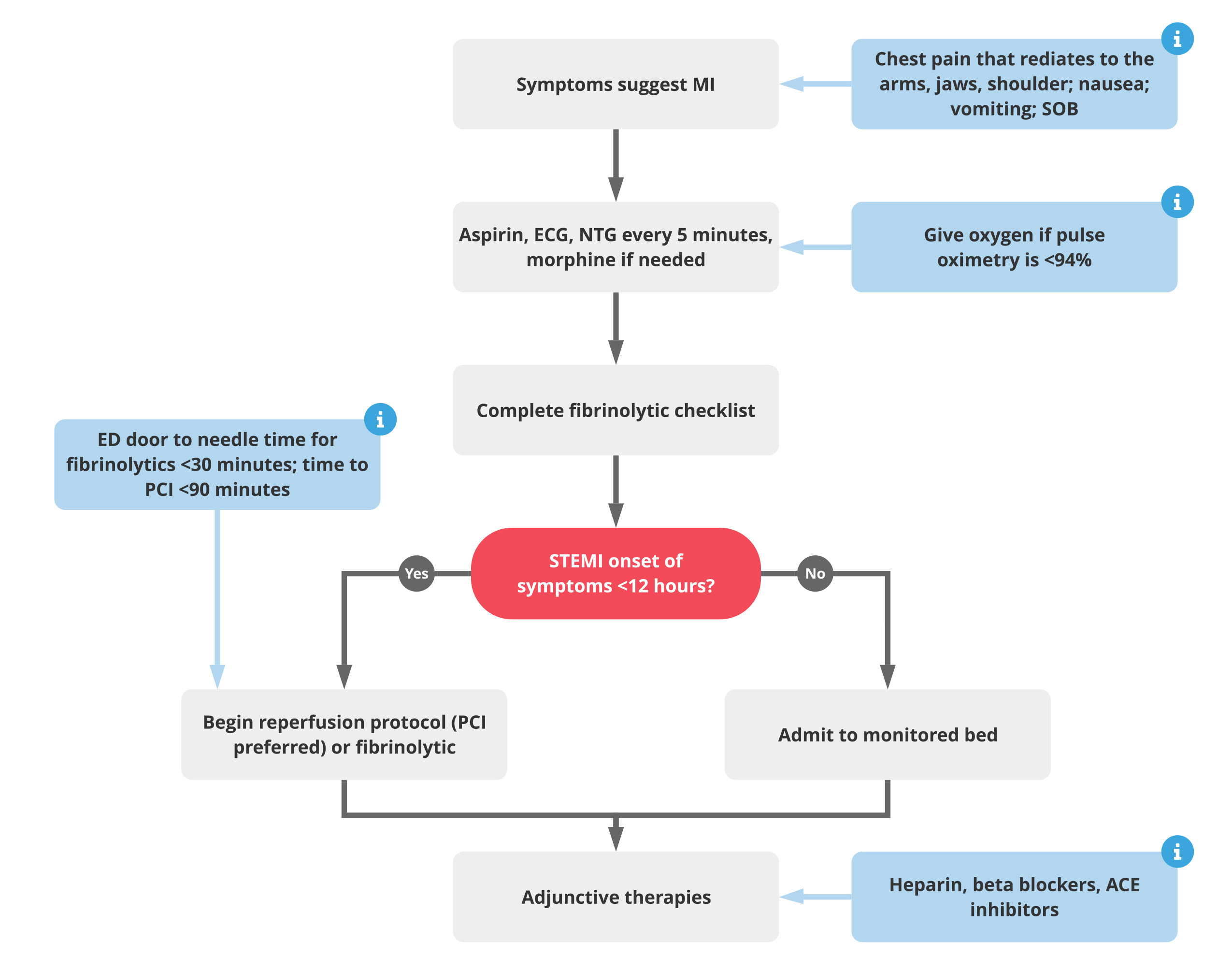
Ment followed by a 75 mg daily dose for up to 8 days in. Compliance with guideline-directed therapy in diabetic patients admitted with acute coronary syndrome. Heparin low-molecular-weight heparin LMWH or un-. Answer The following summarizes the AHA algorithm for emergent treatment of ACS 43. 2014 AHAACC guideline for the management of patients with nonST-elevation acute coronary syndromes. A report of the American College of CardiologyAmerican Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Level of Evidence LOE And Class Matrix Amsterdam E.































Posting Komentar untuk "Acute Coronary Syndrome Treatment Guidelines American Heart Association"