Type Iii Glycogen Storage Disease
Type iii glycogen storage disease. Glycogen storage disease type I also called Von-Gierkes disease is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the. This buildup impairs the function of certain organs and tissues especially the liver and muscles. Glycogen Storage Disease Type III Diagnosis and Management Guidelines created by the AGSD and the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics.
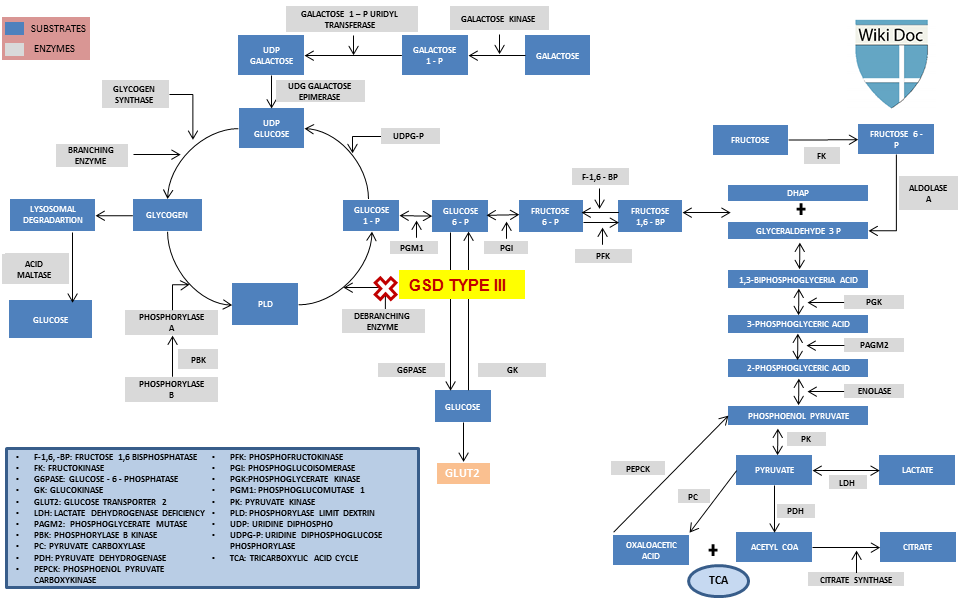
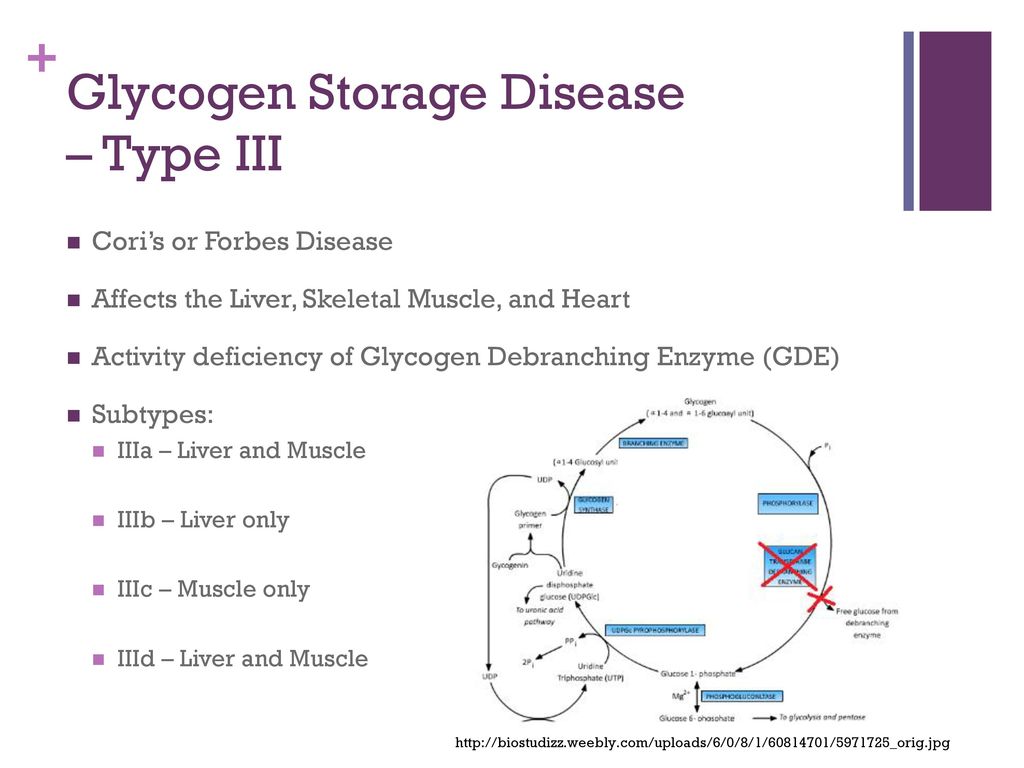
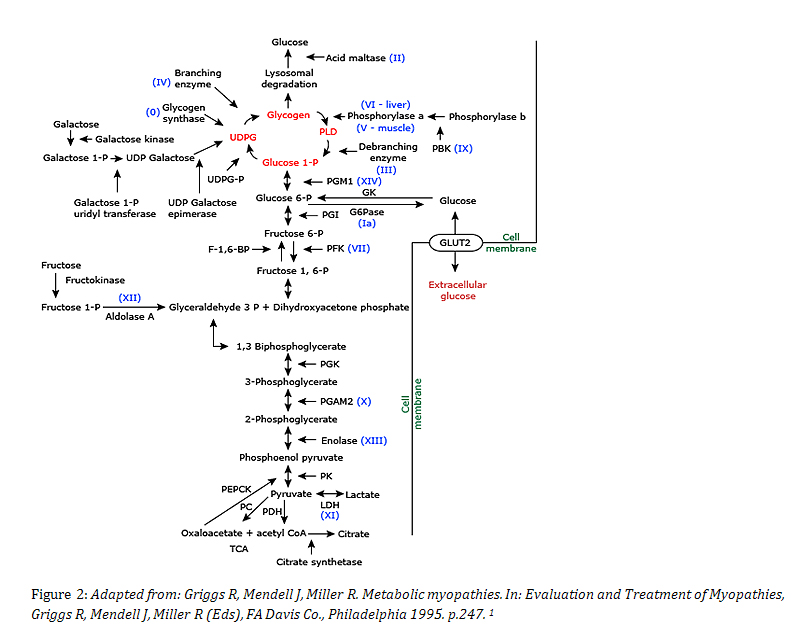
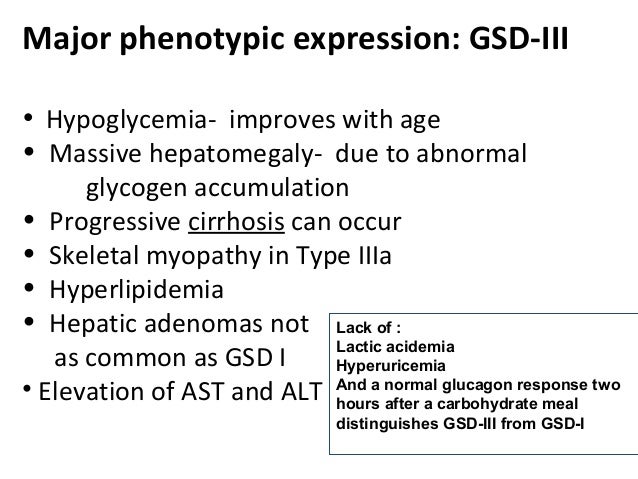
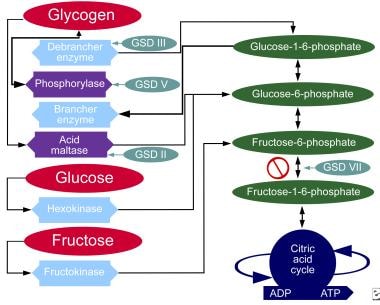
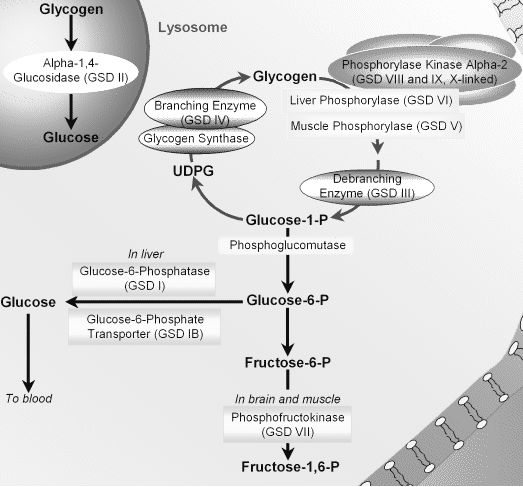
This substance is produced by the action of phosphorylase on glycogen. Glycogen Storage Disease Type III Synonyms of Glycogen Storage Disease Type III. GSD IIIa is the most common subtype present in about 85 of affected individuals.
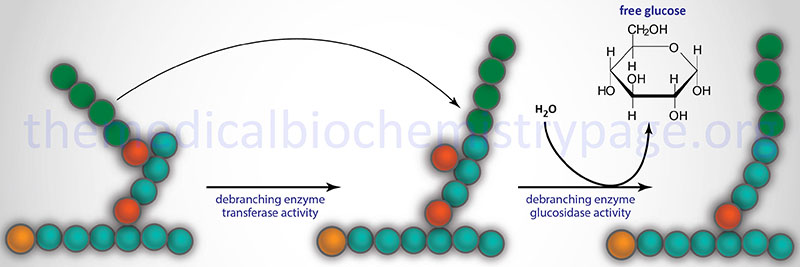
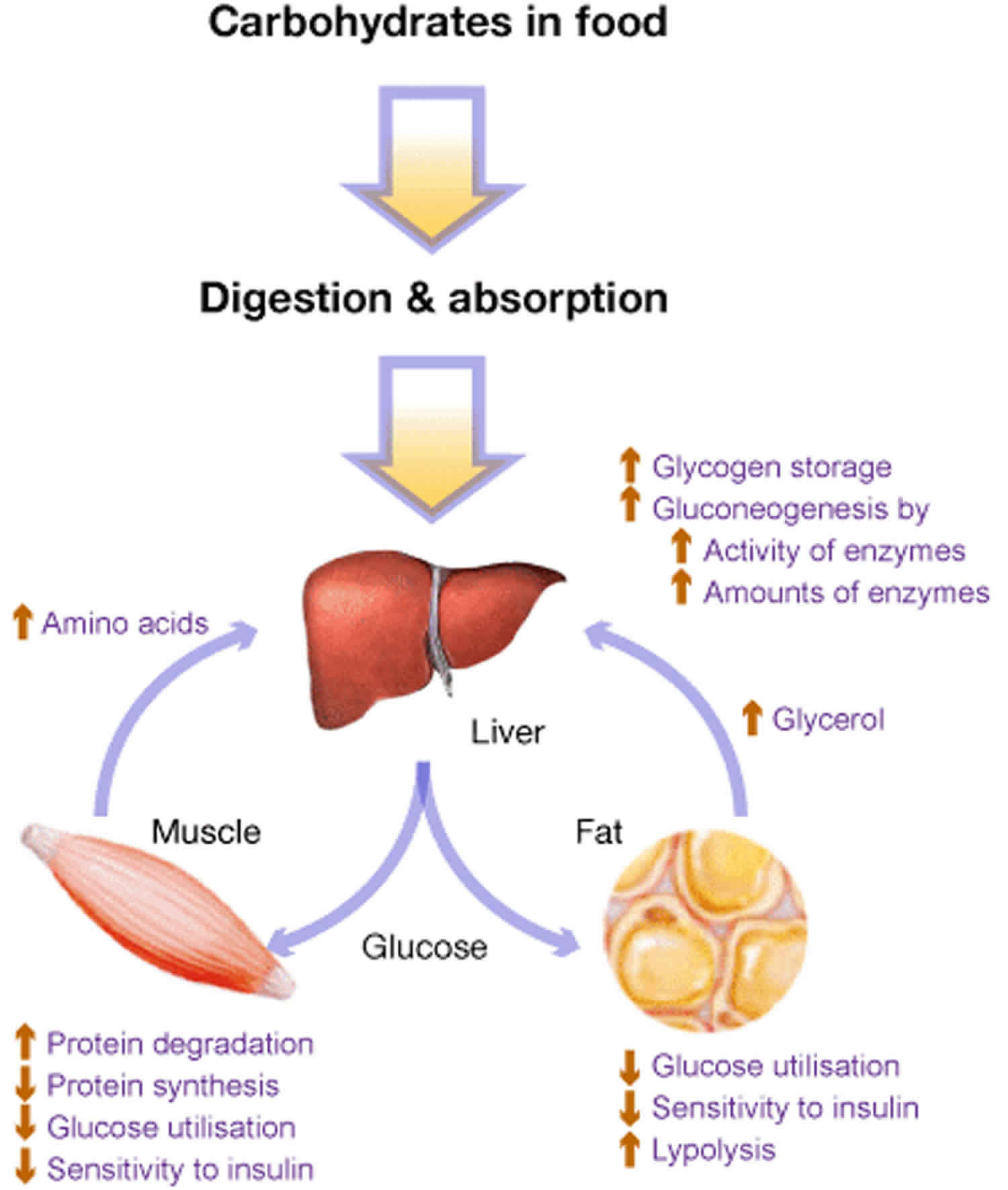
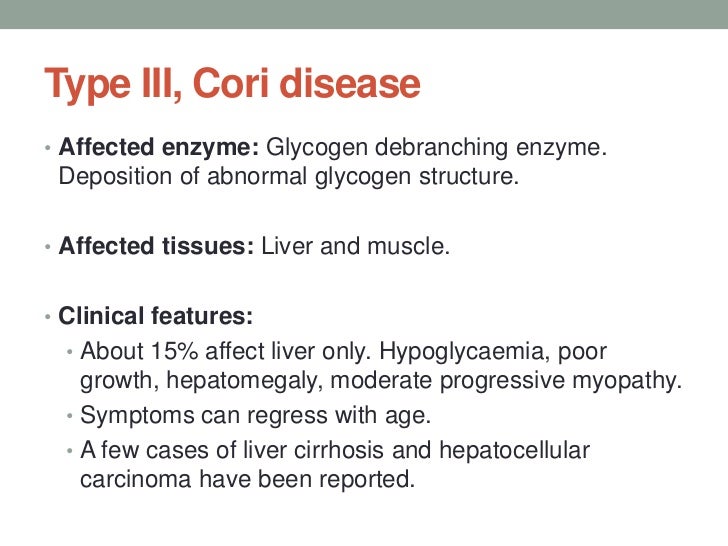
The median age at the first clinical presentations is. The human diet contains 3 macronutrients that can be stored by the body as energy. Glycogen debranching enzyme along with another enzyme phosphorylase helps break down the branches of glycogen to release free glucose.
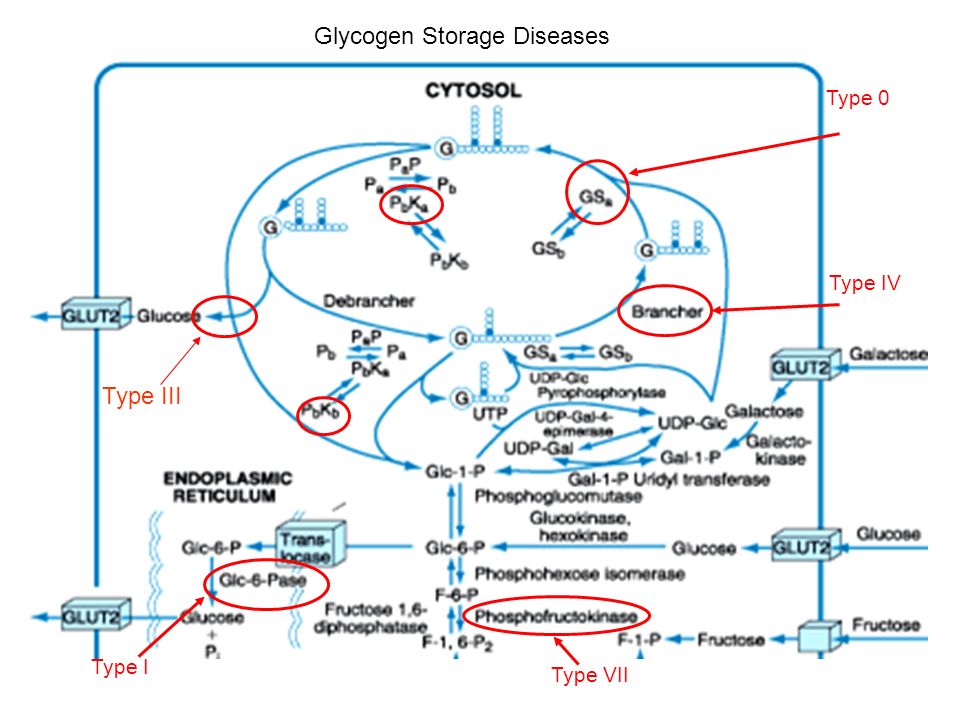
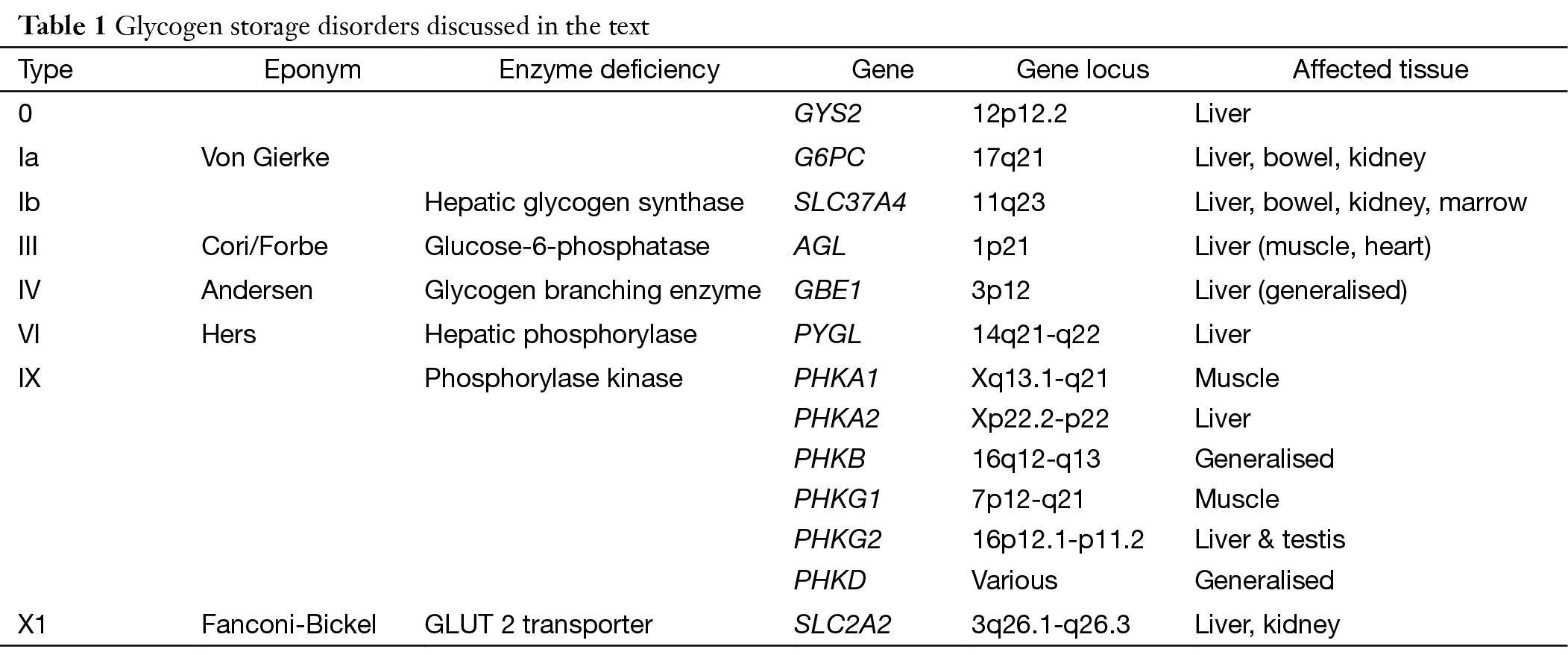
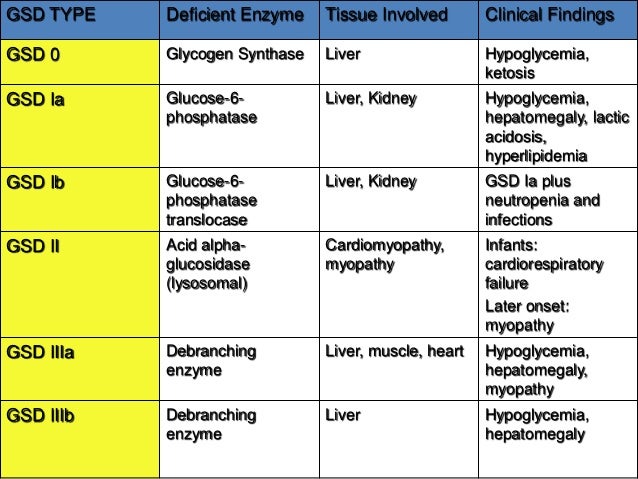
Type III Glycogenosis Limit Dextrinosis. Glycogen storage disease III is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder caused by deficiency of the glycogen debrancher enzyme and associated with an accumulation of abnormal glycogen with short outer chains. In many cases the defect has systemic consequences but in some cases the defect is limited to specific tissues.
Glycogen storage disease type III manifests a wide clinical spectrum. This can create other problems if your child has certain types of GSD such as. Glycogen storage disease type 3 GSD3 is also known as Cori disease Forbes disease and limit dextrinosis.
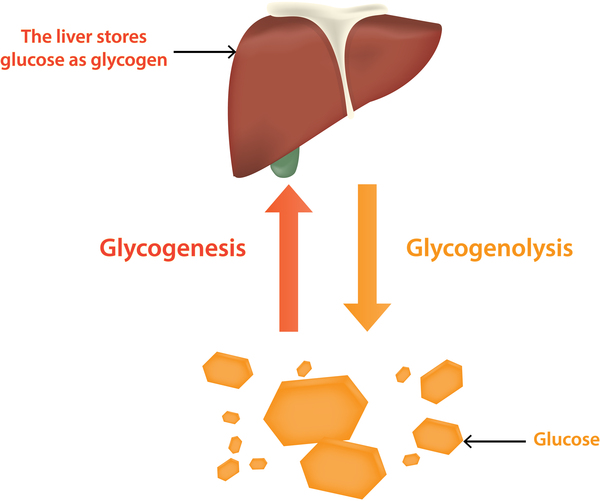
Glycogen storage disease type III GSD III. Glycogen buildup can hurt the liver and muscles. Type III glycogen storage disease is a hereditary disorder with autosomal recessive transmission.
It is an autosomal recessive disease affecting glycogen degradation. Cori disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive disorder.
Glycogen storage disease type III manifests a wide clinical spectrum.
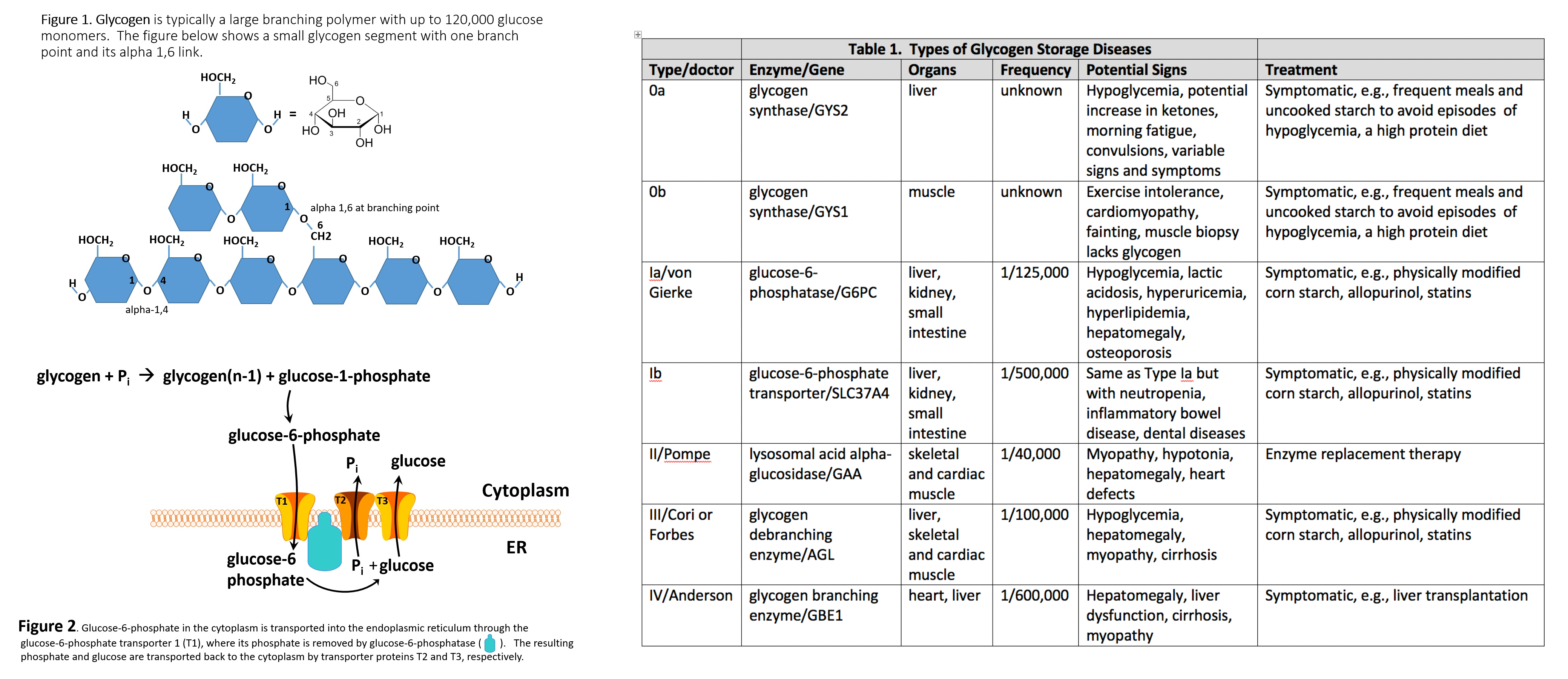
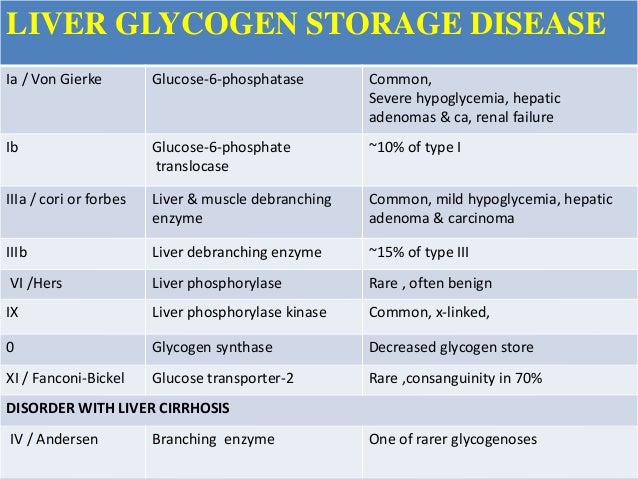
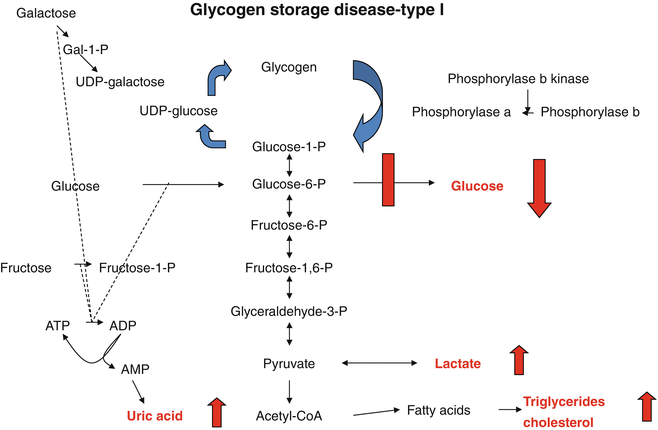
What is glycogen storage disease type I. This buildup impairs the function of certain organs and tissues especially the liver and muscles. Death occurs usually before the ninth month of life. Glycogen debranching enzyme along with another enzyme phosphorylase helps break down the branches of glycogen to release free glucose. It manifests with liver and muscle involvement. Glycogen Storage Disease Type III Diagnosis and Management Guidelines created by the AGSD and the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Type III GSD is caused by a deficiency of glycogen debrancher enzyme GDE activity. Glycogen storage disease type III also known as GSDIII or Cori disease is an inherited disorder caused by the buildup of a complex sugar called glycogen in the bodys cells. It is characterized by accumulation of abnormal glycogen in the liver and in 80 of patients in muscle.
The overall incidence is approximately 1100000 in the United States and 13600 in the Faroe Islands 127. Glycogen storage disease type I also called Von-Gierkes disease is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the. The human diet contains 3 macronutrients that can be stored by the body as energy. In many cases the defect has systemic consequences but in some cases the defect is limited to specific tissues. Cori disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive disorder. Over time this can cause scarring cirrhosis of the liver. It is characterized by accumulation of abnormal glycogen in the liver and in 80 of patients in muscle.




























Posting Komentar untuk "Type Iii Glycogen Storage Disease"